
The use of silicon steel (also known as electrical steel, lamination steel) is increasing year by year. As a steel type used in very specific industries, the key indicators of silicon steel are directly reflected by the grades.
Therefore, to understand the naming rules of grades and the meaning of key indicators will help us understand the products in a more effective way.

What's the core indicator of electrical steel? ----Low iron loss. During the energy conversion process of magnetism and electricity, energy could be lost in forms of heat, noise and so on. All properties related to loss are key indicators of silicon steel.
The naming of silicon steel grades usually includes four indicators: thickness, type, iron loss, and coating.
Take one of our non grain oriented silicon steel grades for an example:
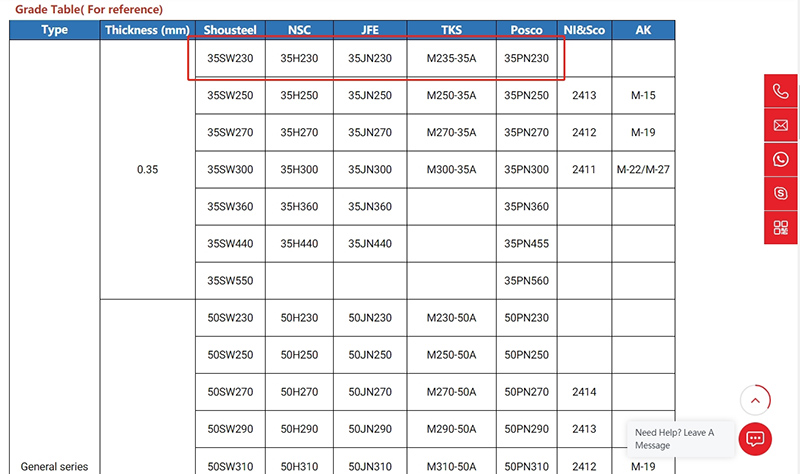
Check out the first row marked red.
The naming rules of 35SW230 consist of “thickness-brand-type-iron loss”:
“35” indicates thickness is 0.35mm,
“S” stands for Shou steel, which is the manufacturer,
“W” stands for non grain oriented silicon steel,
“230” is the iron loss value for reference.

These four indicators - thickness, type, iron loss and coating will have different effects on price and application:
Thickness:
With thinner thickness, the eddy current loss (heating) in the iron loss would be less, which means the production difficulty would be higher, therefore the silicon steel price would be higher;
For example, under the same conditions, 0.35mm material is more expensive than that of 0.5mm.
Type:
Shunge steel provides ordinary non-oriented, intermediate frequency non-oriented, oriented silicon steel, etc. Different types are used in different products to satisfy different requirements;
Iron loss:
Iron loss refers to the energy lost in the process of energy conversion after the iron core material is added with a certain alternating magnetic field. The lower the value is, the less loss and the more expensive the price would be.
For example, the same 0.35mm conventional non-oriented electrical steel, 35SW230 is more expensive than 35SW550.
Coating:
The coating of silicon steel mainly plays an insulating role. Taking oriented silicon steel as an example, different coatings have different characteristics and applications, and the prices would also vary slightly.
For example, common non-oriented silicon steel coatings include thin coatings, thick coatings, extremely thick coatings, self-adhesive coatings, etc., as well as corresponding chrome-free environmental protection products.
As a matter of fact, while selecting the electrical steel, the coating is an indicator that is frequently ignored. Due to ignoring the coating, some losses occur during manufacturing and other practical applications.
For example, manufacturer's process originally needed a semi-organic thin coating that can withstand stress relief annealing temperatures up to 800°C. However, without asking more questions about coatings, mispurchasing self-bonding coatings could cause quality issues. Because self-bonding coatings cannot withstand normal stress-relief annealing temperatures.
In some cases, the manufacturer originally needed a semi-organic thin coating, but purchased an ultra-thick coating by mistake, which caused the result that manufacturing process emitting a very strong smell during the aluminum pouring process, which eventually led to quality disputes.
You might have noticed that he words “P1.5/50” and “P1.7/50” are often seen in the iron loss description of the silicon steel grade.
Because in some countries where the main frequency is 50Hz, P1.5/50 and P1.7/50 are respectively used to characterize the iron loss characteristics of non-oriented silicon steel and oriented silicon steel.
That is to say, P1.5/50 usually means non oriented , and P1.7/50 usually means oriented.
Why is the iron core stacked with silicon steel sheets?
As is shown in the picture below, if the iron core is stacked with silicon steel sheets, the heat loss caused by eddy currents can be effectively reduced.
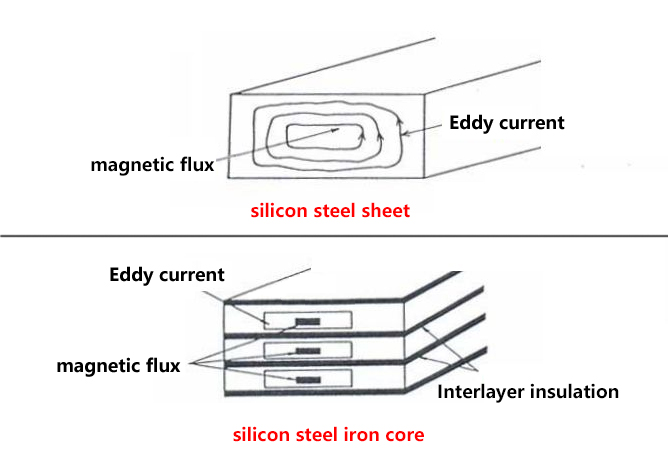

Knowing the meaning of different figures of silicon steel is great help of selecting the proper steel in an cost effective way.
Or, if you still struggling of finding the proper one, contact us and send us all the needs, we will try our best to recommend the ideal steel for you.
We will contact you as soon as possible
Hi! Click one of our members below to chat on