 Selecting of steel
Selecting of steel
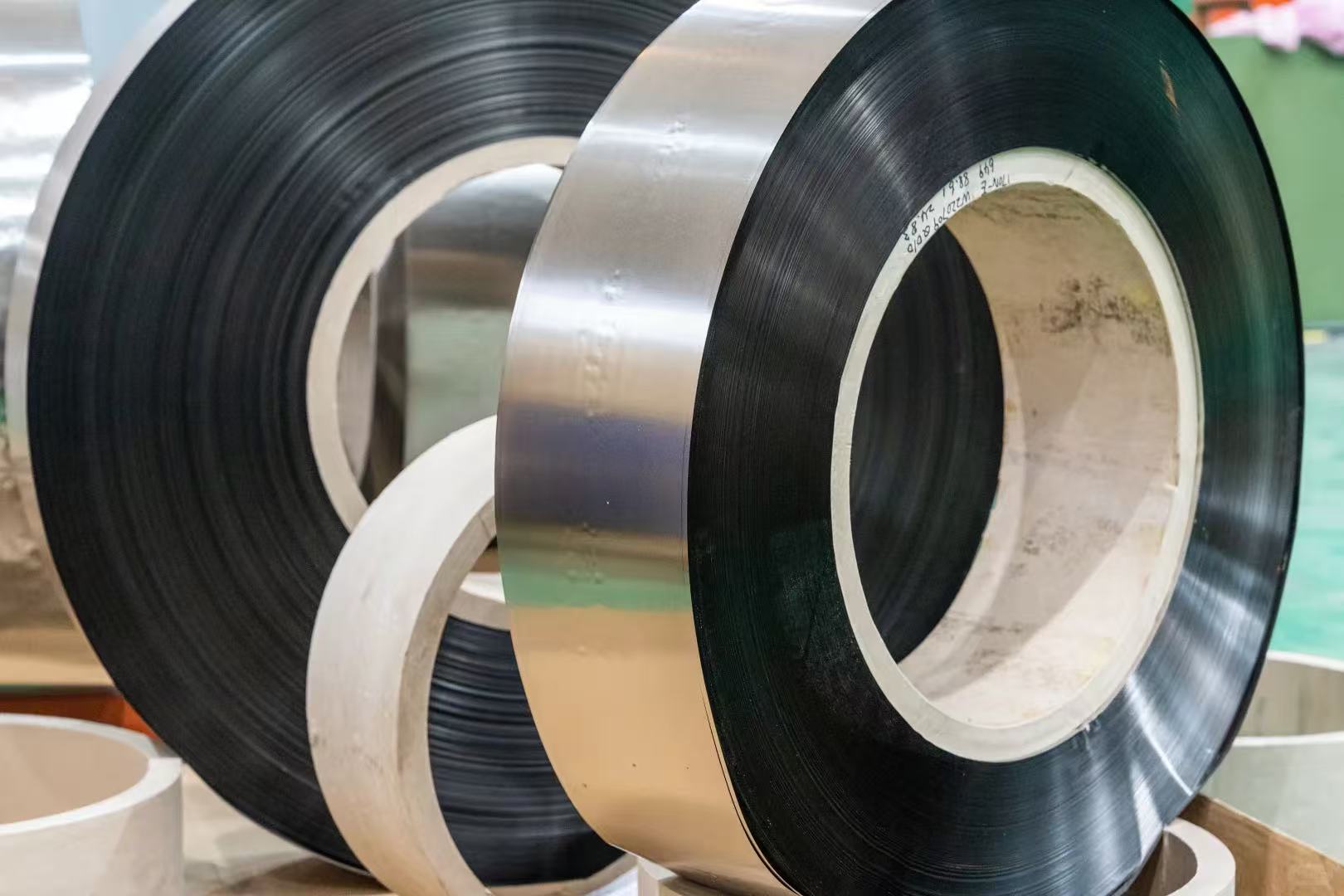 ASTM standard silicon steel coils providing core power for high-efficiency electrical equipment
ASTM standard silicon steel coils providing core power for high-efficiency electrical equipment
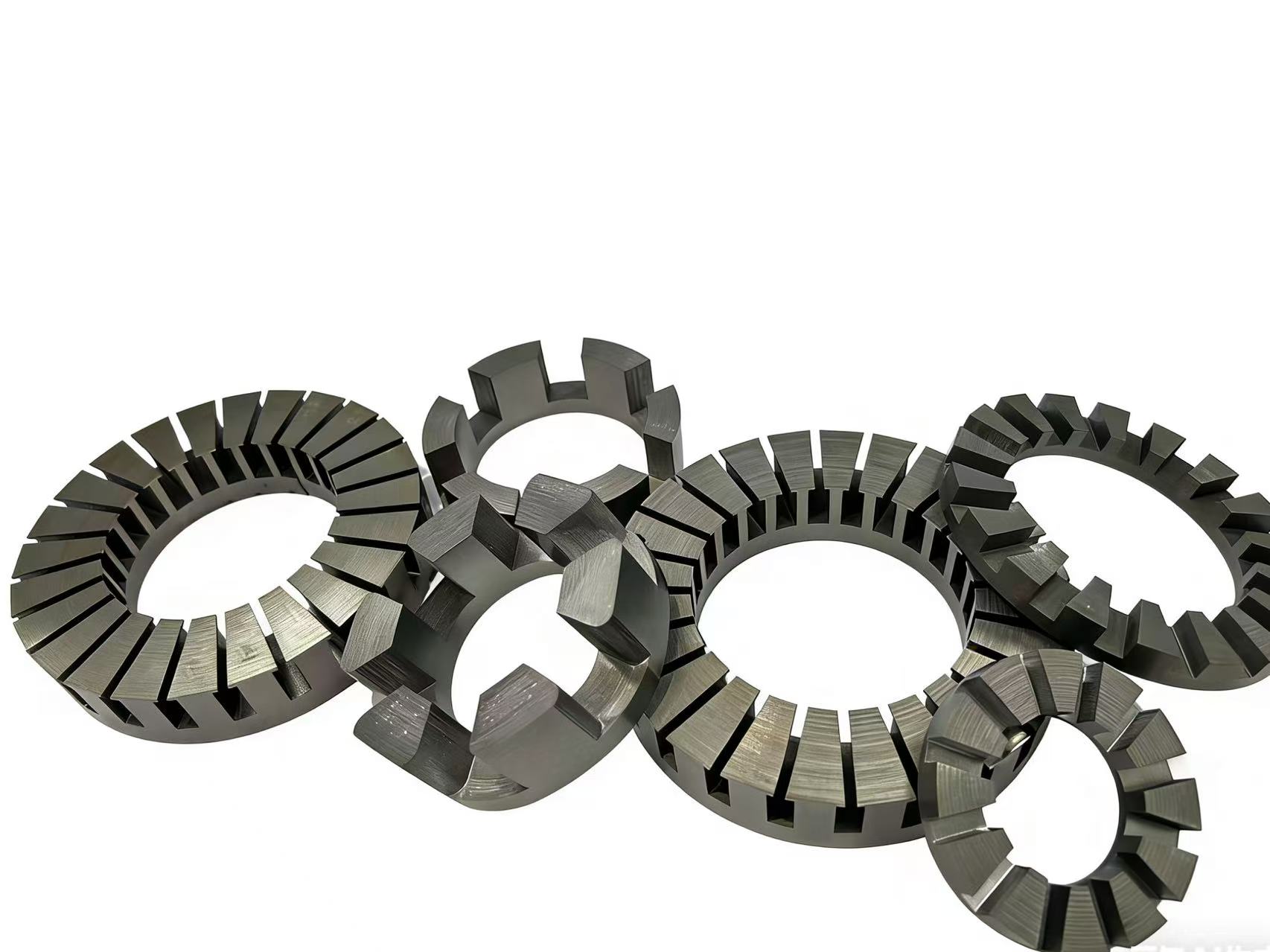 Low-iron-loss motor laminated silicon steel helps new energy vehicles achieve a leap in performance.
Low-iron-loss motor laminated silicon steel helps new energy vehicles achieve a leap in performance.
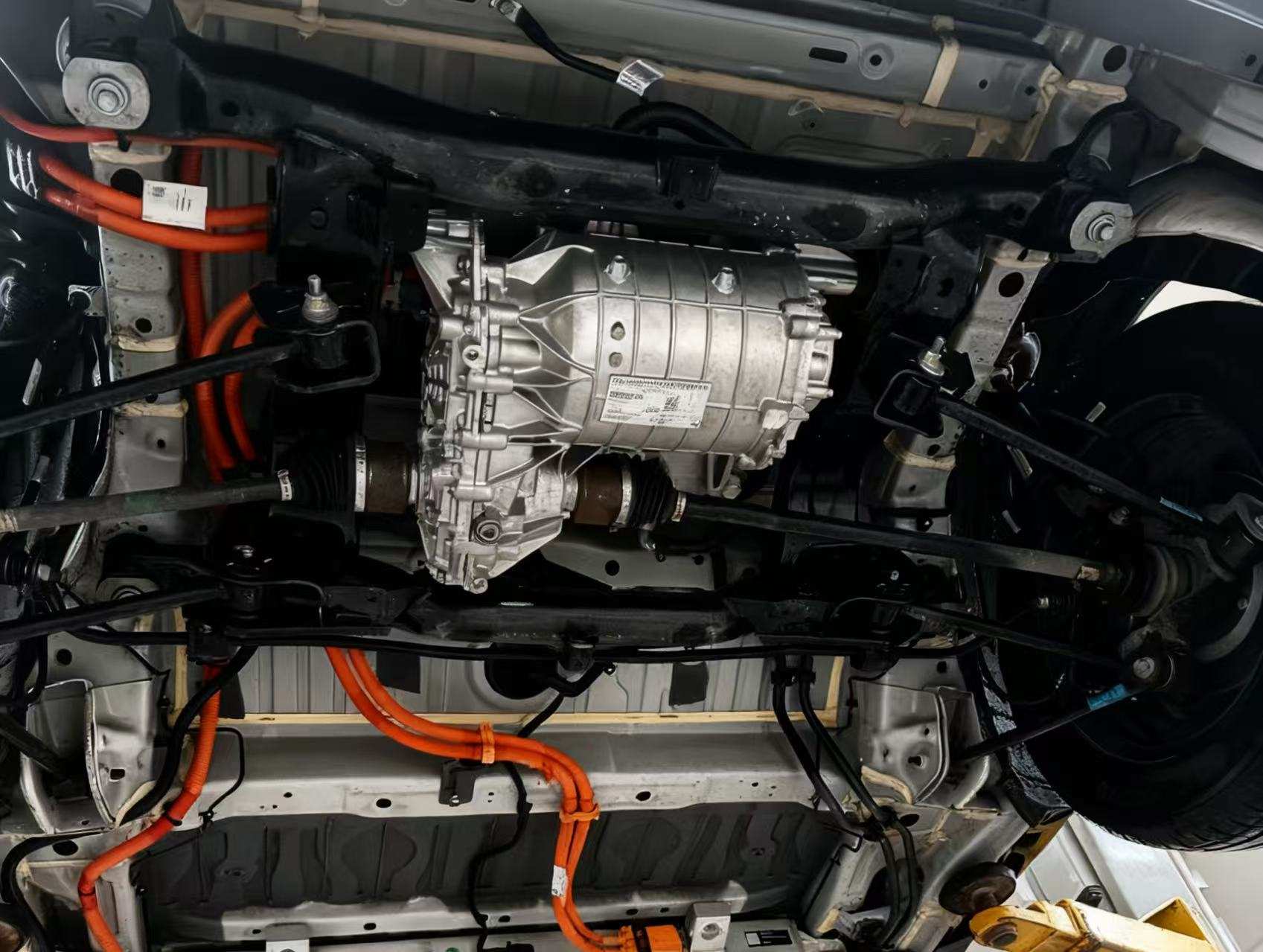 Application scenarios of silicon steel for new energy vehicles
Application scenarios of silicon steel for new energy vehicles
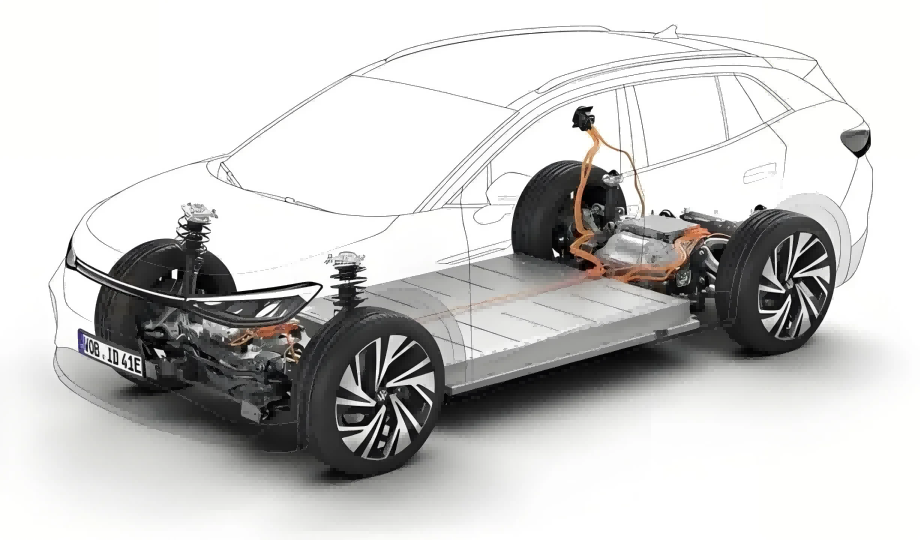 Application of ultra-thin silicon steel (0.1-0.2mm) in new energy vehicles
Application of ultra-thin silicon steel (0.1-0.2mm) in new energy vehicles
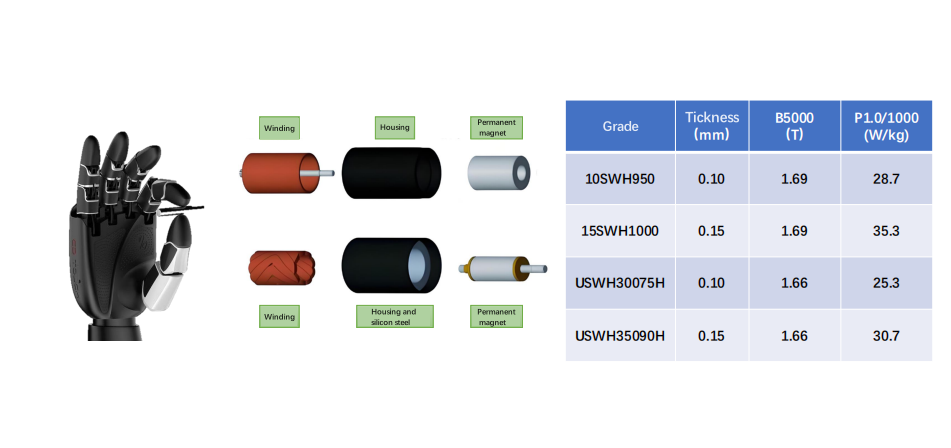 Applications of ultra-thin silicon steel (0.1-0.2mm) in the field of humanoid robots
Applications of ultra-thin silicon steel (0.1-0.2mm) in the field of humanoid robots
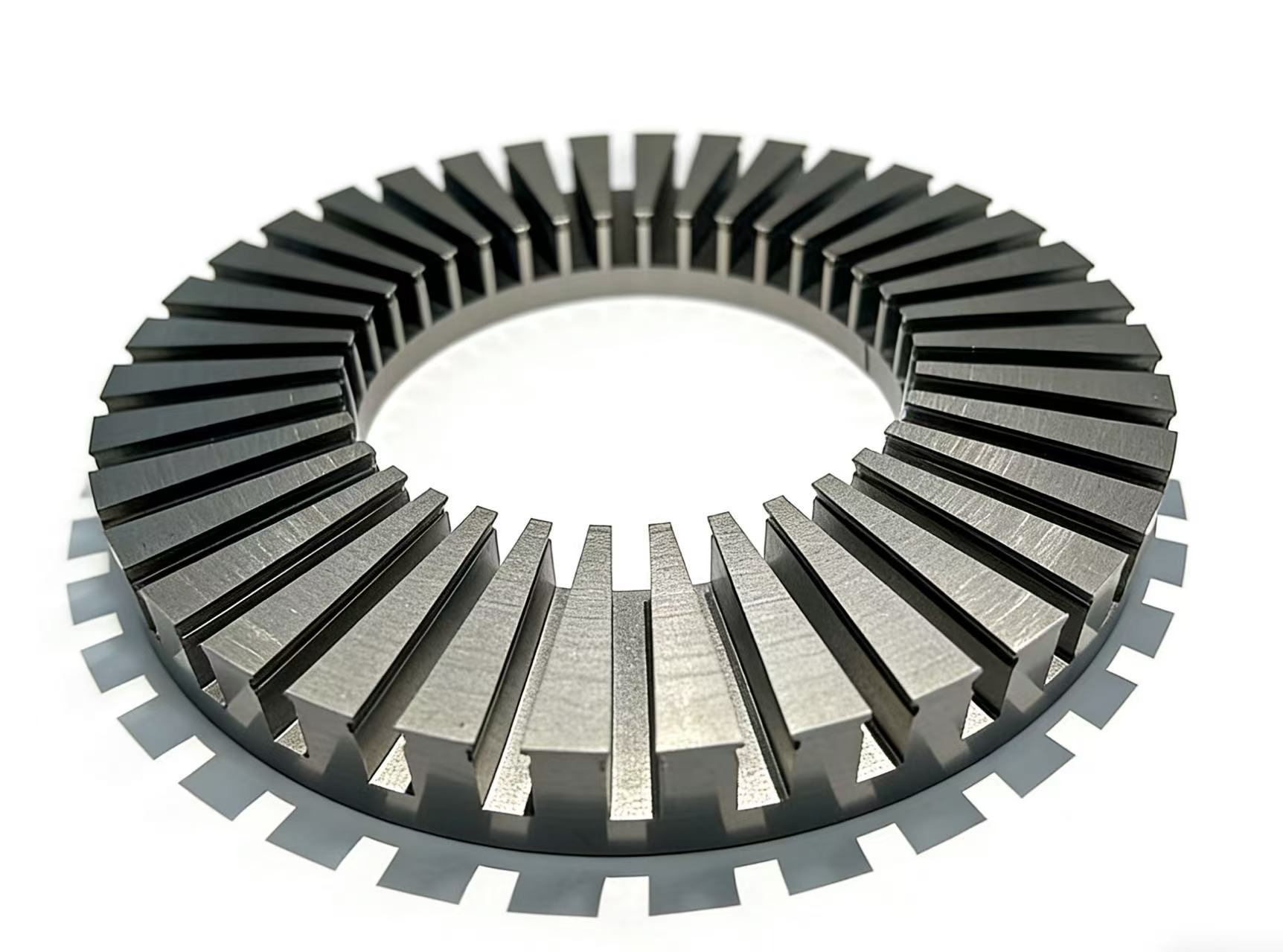 Advantages and applications of self-adhesive coating technology for ultra-thin silicon steel.
Advantages and applications of self-adhesive coating technology for ultra-thin silicon steel.
 What are the advantages of using ultra-thin silicon steel in axial cores
What are the advantages of using ultra-thin silicon steel in axial cores
 In which fields is ultra-thin silicon steel (0.1-0.2mm) used
In which fields is ultra-thin silicon steel (0.1-0.2mm) used
 What are the advantages of ultra-thin silicon steel (0.1-0.2mm)?
What are the advantages of ultra-thin silicon steel (0.1-0.2mm)?
 Why Pursue "Ultra-thin" Silicon Steel?
Why Pursue "Ultra-thin" Silicon Steel?
 Why pursue ultra-thin non-oriented silicon steel?What are the key advantages of this design?
Why pursue ultra-thin non-oriented silicon steel?What are the key advantages of this design?
We will contact you as soon as possible
Hi! Click one of our members below to chat on